
Click the topic to read previous chapters:
Chapter I: Overview of AI Technology

Chapter II
AI Industry Policies, All-Round Protection of Intellectual Property Rights and Patent Spplication Trends in Major Countries & Regions
With the constant changes and improvements of artificial intelligence (AI) technology, all countries around the world are paying close attention to and actively introducing relevant policies to provide environmental and policy support for the rapid development of AI technology, and are taking the initiative to explore feasible plans and corresponding protection and response mechanisms in terms of those ignorable ethical and moral issues brought by AI technology. Unarguably, the irreplaceable status of AI technology in the fourth global industrial revolution and the leadership of AI technology in future strategy will quickly promote the application of AI in various fields, thus laying a foundation for epoch-making scientific progress in the world. Accordingly, AI-related patent applications are growing rapidly in number, covering various technical fields related to AI.
2.1 AI Industry related Policies in Major Countries and Regions
If the birth of the discipline of modern artificial intelligence is to be marked with the earliest appearance of the term “Artificial Intelligence (AI)”, it should be in Dartmouth Artificial Intelligence Conference initiated in 1955 and held in 1956. It is generally accepted that AI was formally proposed by John McCarthy, convener of the conference.[1] This conference aimed at calling like-minded people together to discuss “AI”. In the proposal of this conference, McCarthy et al. said that “We propose that a 2-month, 10-man study of artificial intelligence be carried out during the summer of 1956 at Dartmouth College in Hanover, New Hampshire. The study is to proceed on the basis of the conjecture that every aspect of learning or any other feature of intelligence can in principle be so precisely described that a machine can be made to simulate it. An attempt will be made to find how to make machines use language, form abstractions and concepts, solve kinds of problems now reserved for humans, and improve themselves.[2]” This conference lasted for a month, basically focusing on a large-scale brainstorming. This gave birth to the AI revolution known to all.
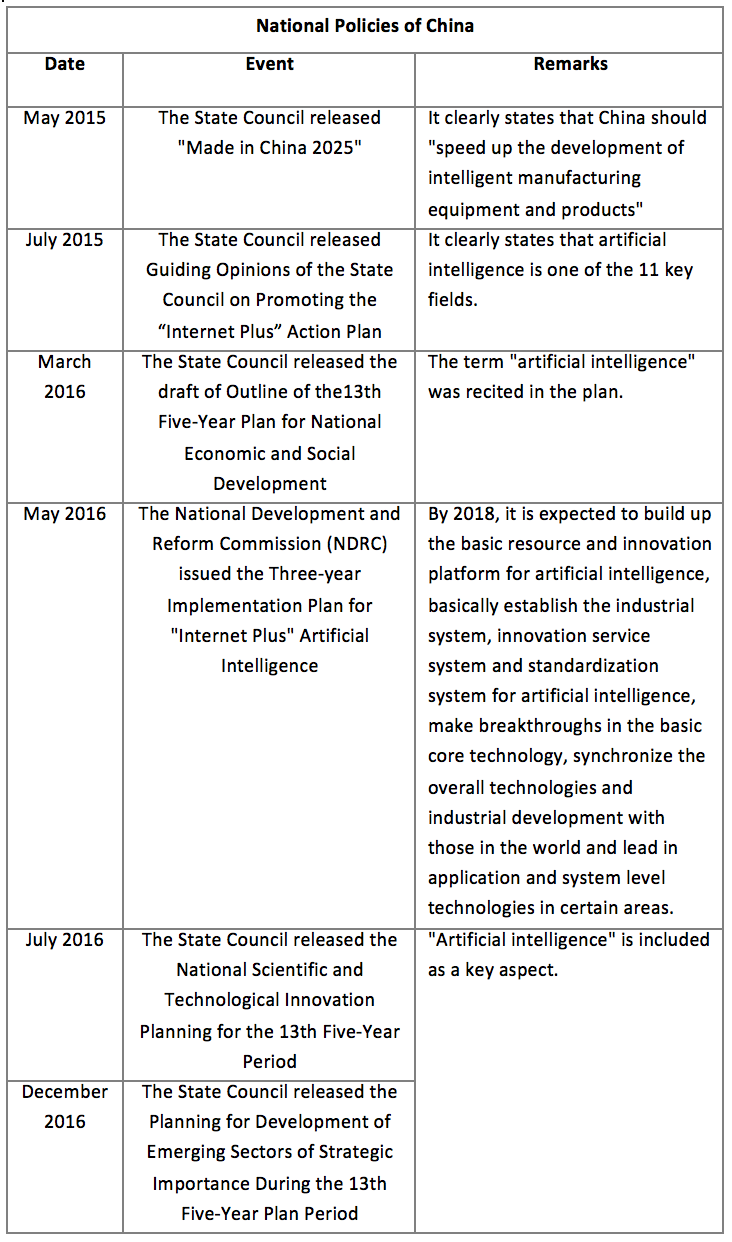
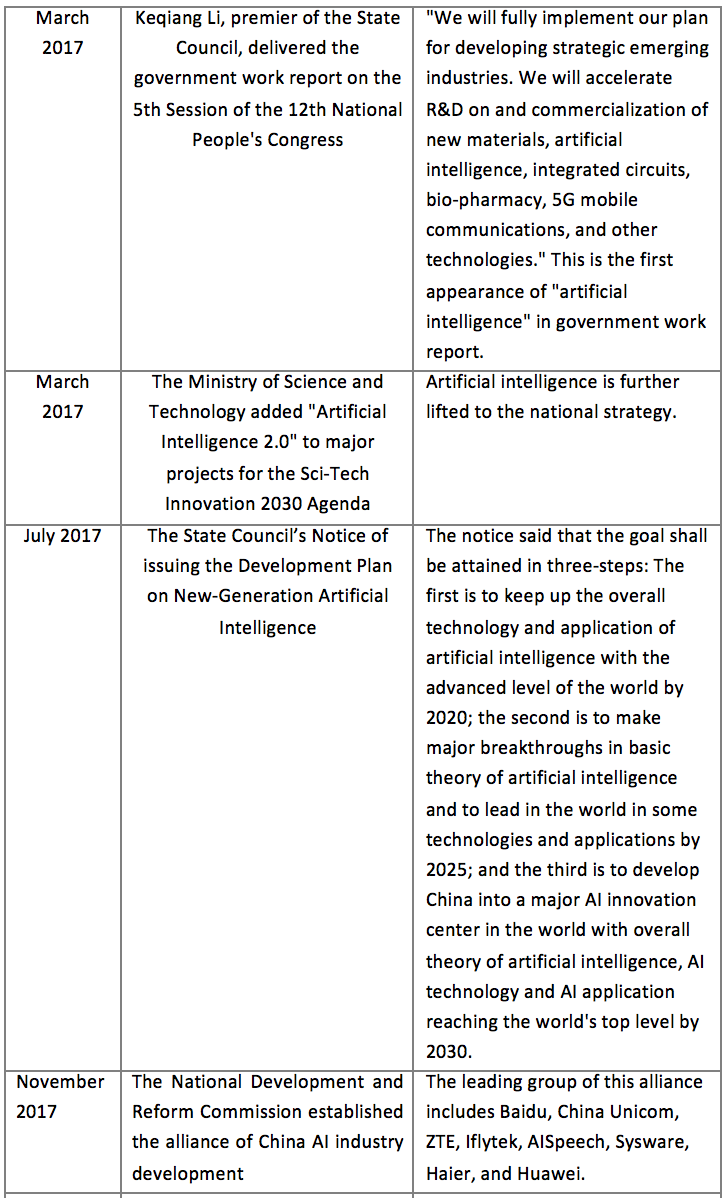
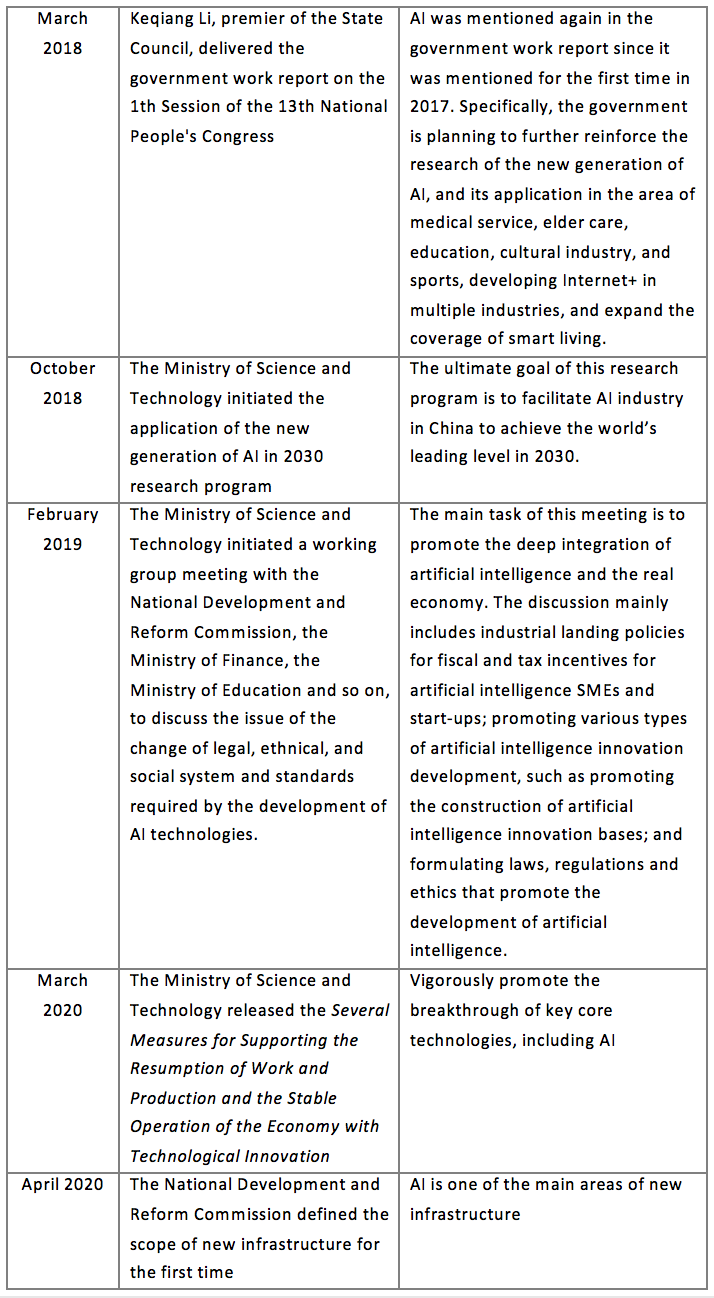
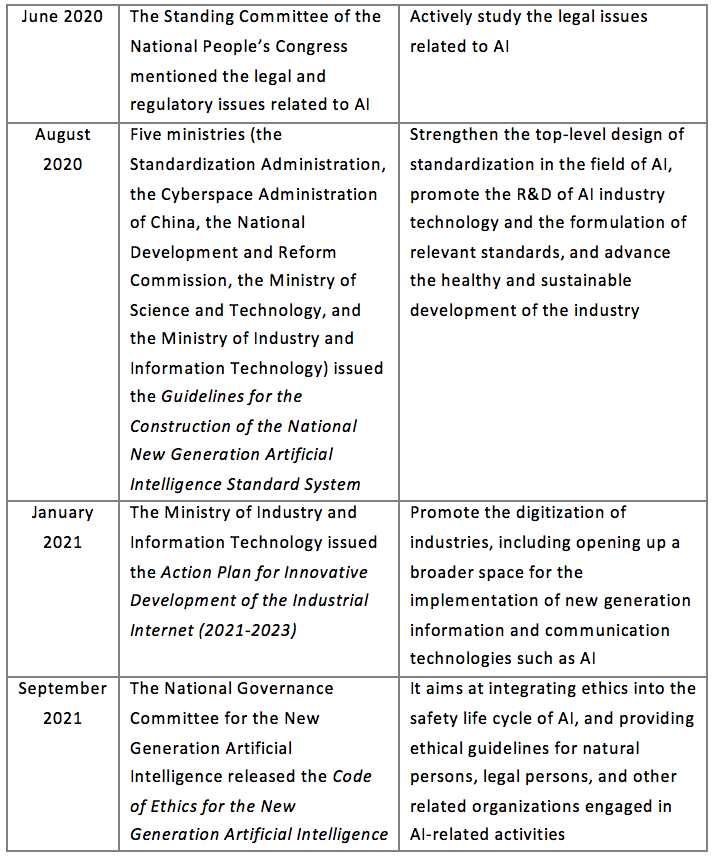
2.1.1 China
The Chinese government attaches great importance to the development of AI, actively promoting the construction of standards for AI industry, inter-industry integrated, co-created and shared intelligent economic pattern, and advocating the establishment of a new order for the development of the intelligent industry in a standardized, orderly, safe and sound manner at the government level.
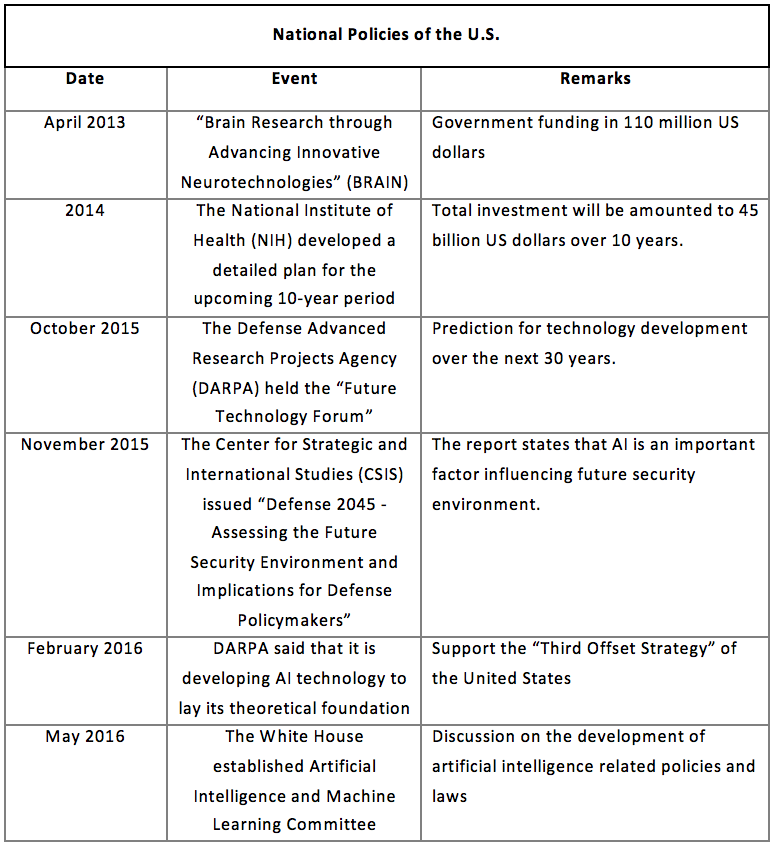
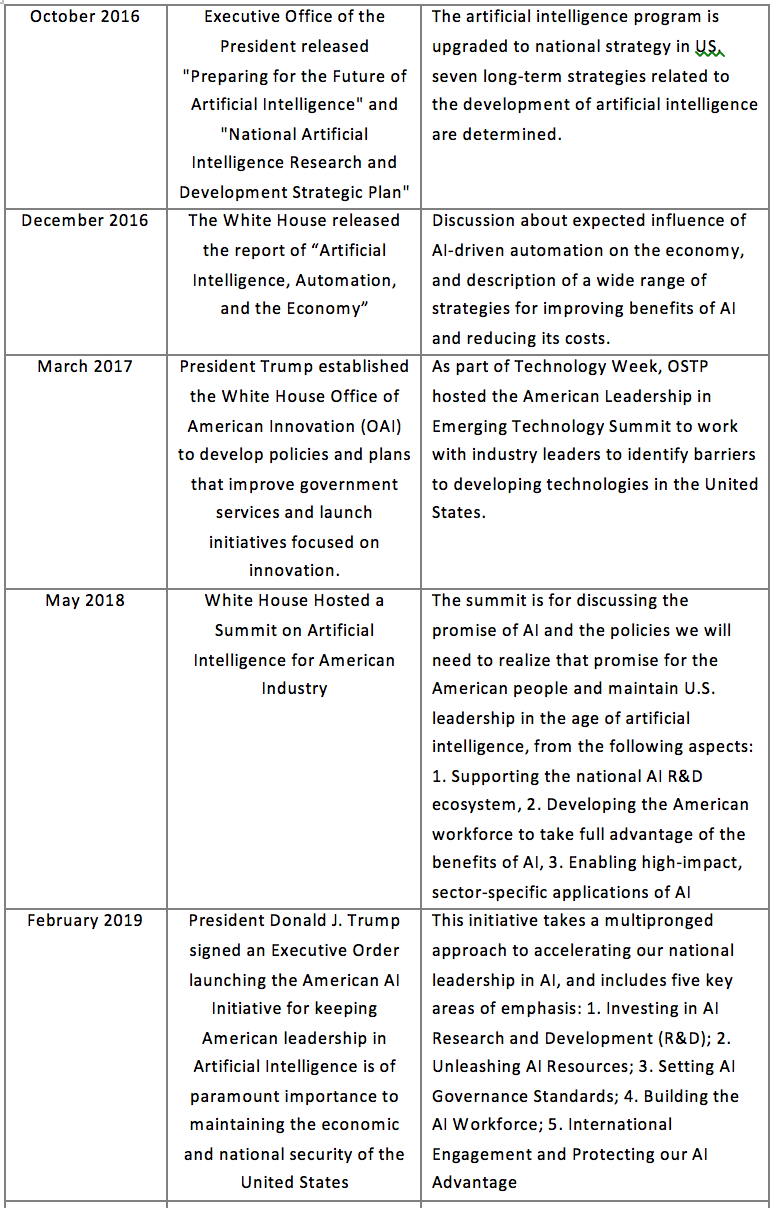
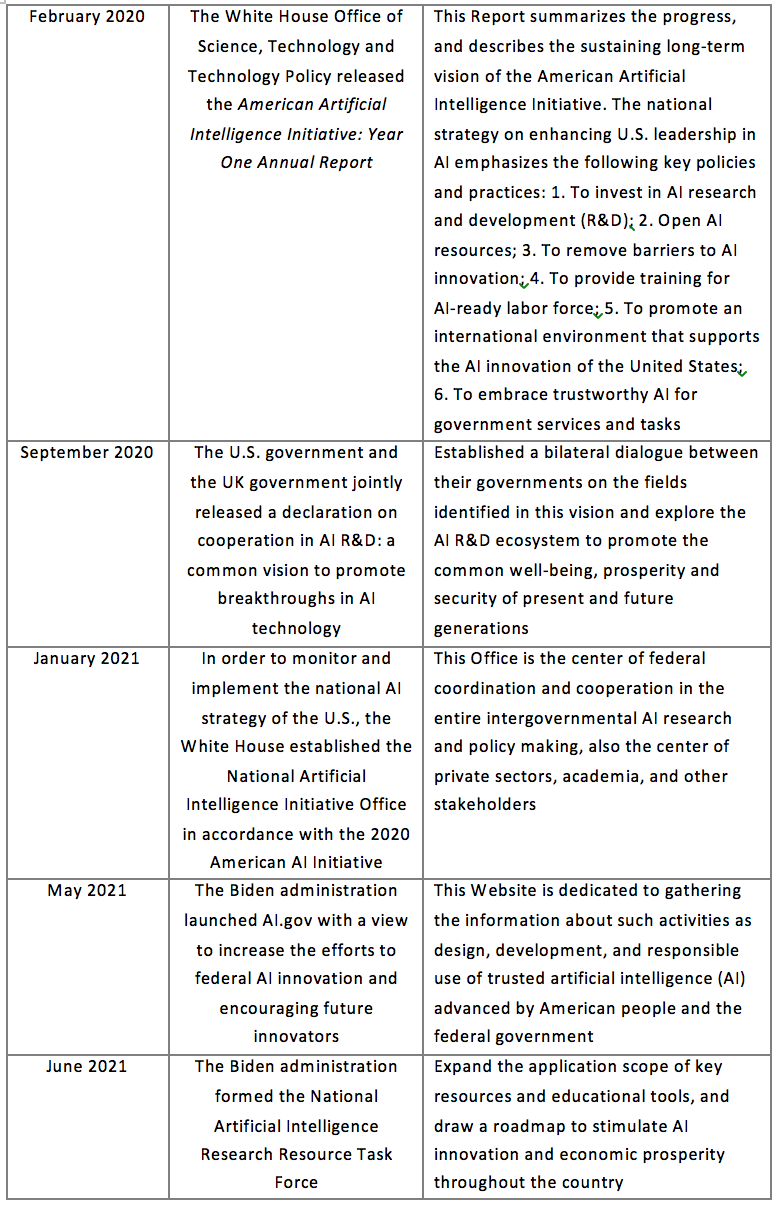
2.1.2 The United States
Although the U.S. government has invested a lot of funds and taken a lot of safeguard measures for the development of AI early on in terms of funds and policies, a report adopted by vote by the National Security Commission on Artificial Intelligence (NSCAI) in March this year pointed out that the U.S. government is “unprepared” in responding to the new threats of AI and thus must implement major changes. Therefore, it is foreseeable that the United States will invest more funds and provide more support for the development of AI in the future.
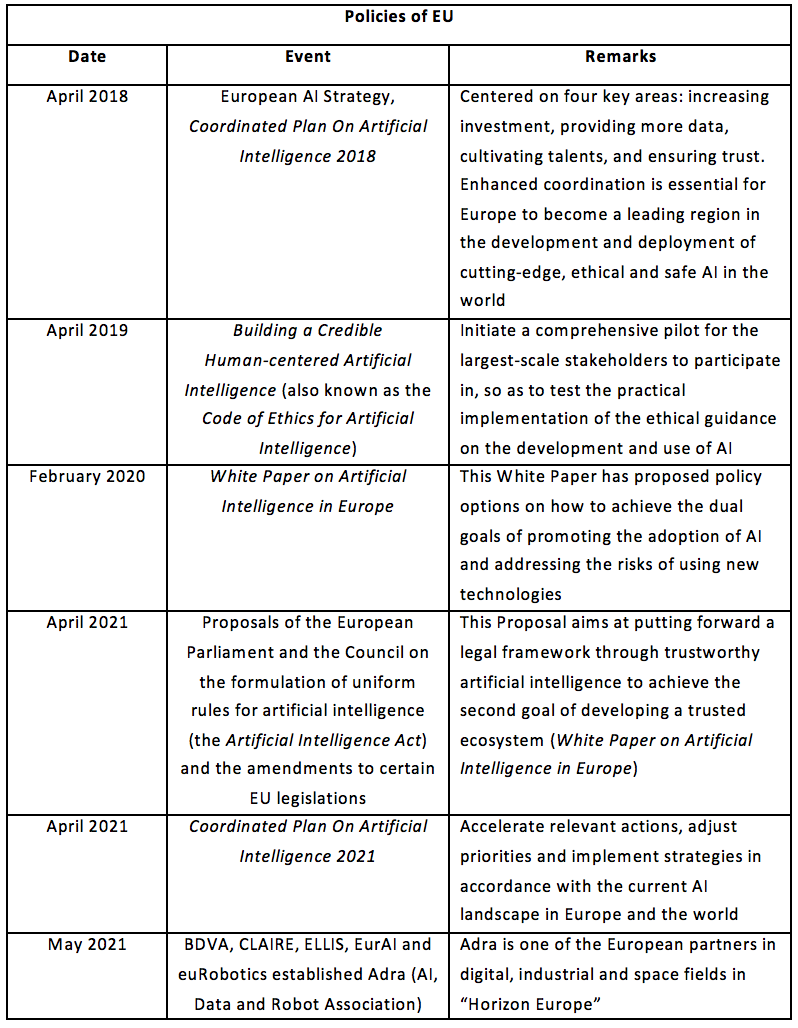
2.1.3 Europe
In order to promote research, the European Union increases the investment in AI continuousely, supports investors from different industries in jointly making collaboration plans, and stimulates the application of AI in fields such as public service and academic research, in the hope of accelerating the derivation of successful products, services and collaboration networks through these practices.

2.1.4 Japan
From the layout of AI in Japan, it can be seen that the Japanese government attaches great importance to the top-level design and strategy in terms of research and development, and hopes to maintain and expand its technical advantages, gradually solve social problems such as aging, labor shortage, medical care and elder-care, and build a “Super Intelligent Society” by striving to develop AI.
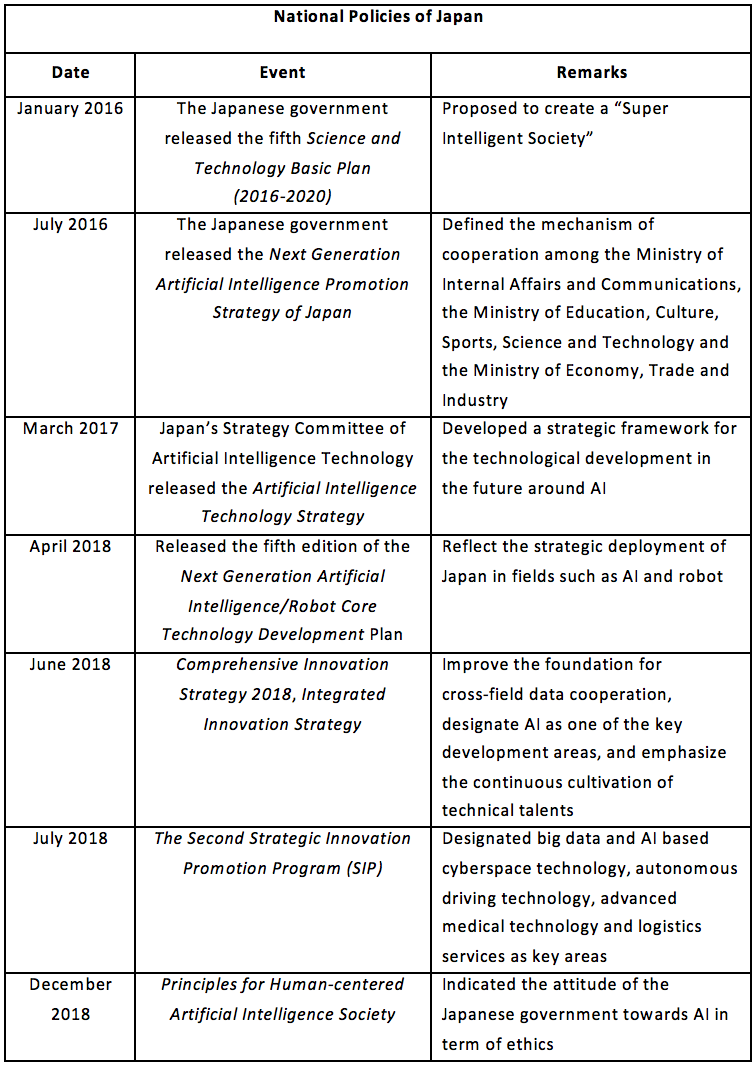
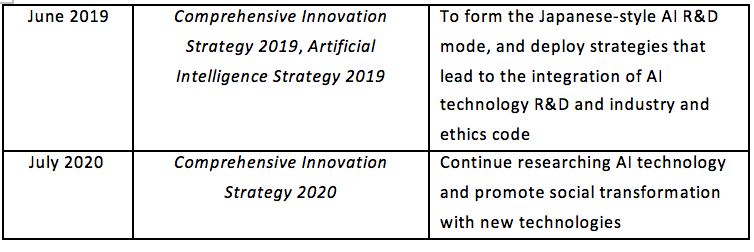
2.1.5 South Korea
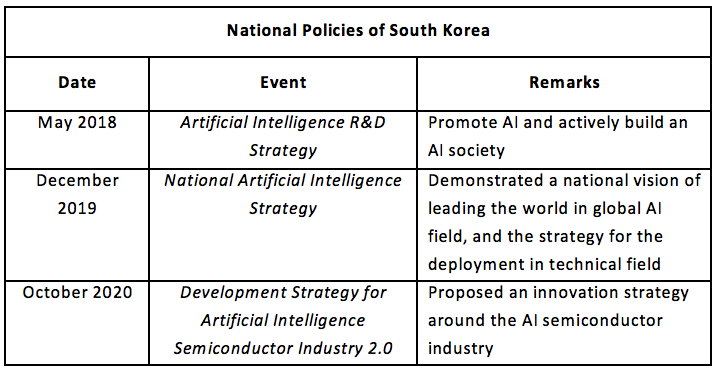
In order to accelerate innovation and development, and inject new vitality into the industry, the Korean government attaches great importance to the development of AI technology, and announced the National Artificial Intelligence Strategy in 2019, with a view to gathering national strength to realize the transformation from an “IT power” to an “AI power”. On October 12, 2020, South Korea released the Development Strategy for Artificial Intelligence Semiconductor Industry (System Chip Outlook and Strategy 2.0) jointly formulated by relevant departments including the Ministry of Science and ICT at the 13th Science and Technology Ministers’ Conference. This Strategy defined the vision of “marching toward a leading country in AI semiconductors and realizing the goal of becoming an AI and comprehensive semiconductor power”, and the goal of possessing a global market share of 20%, 20 innovative enterprises, and cultivating 3000 high-level talents by 2030.
2.2 All-Round Protection of AI Intellectual Property Rights
The above part hereof has outlined AI technology and the AI industry policies in major countries. The following chapters will provide all-round protection schemes for intellectual property rights in AI field, introductions to and suggestions on the main types of intellectual property protection from the macro to the micro based on the technical characteristics of AI field.
2.2.1 All-Round Protection Schemes for AI Intellectual Property Rights
Concept of the layout of intellectual property rights: Layout of intellectual property rights is a top-level planning and guiding ideology for constructing intellectual property portfolios, and is an overall strategic consideration, which includes both large layout for overall consideration, as well as small layout for a certain product or a certain project.
The core objective of the intellectual property layout is to facilitate competition and cooperation in the business to the maximum extent.
Currently, there are not many lawsuits in the field of artificial intelligence, which is mainly due to the following reasons. On one hand, there is an endless stream of technological innovations related to artificial intelligence while all market players are still in the stage of obtaining their rights at present and they all are rushing to claim their share in new markets; on the other hand, related applications and markets are still in a very early stages and competition now is not so fierce. However, it is foreseeable that, with popularization of artificial intelligence applications and the increasingly fierce market competition, patent war in AI field will be inevitable in the future and may overshadow the litigations in the mobile Internet era.
According to the characteristics of AI field, it is advisable to select a combination of various suitable types of intellectual property, and establish an all-round intellectual property protection system involving patent, trademark, copyright, domain name, trade secret and defensive disclosure so as to prepare for the intellectual property competition in the future.
According to the characteristics of AI field, in the rich land of AI, it is advisable to select a combination of various suitable types of intellectual property, and establish an all-round intellectual property protection system involving patent, trademark, copyright, domain name, trade secret and defensive disclosure so as to prepare for the intellectual property competition in the future.
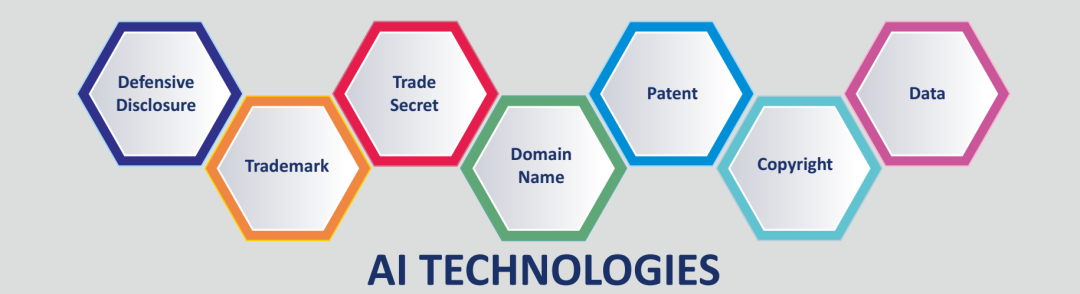
Fig. 2.2.1-1
· Patent (Invention, Utility Model, and Design): It is the most common form of intellectual property protection, and represents core competitiveness of enterprises since it allows for exclusive ownership of core innovations, and also brings about intangible assets for the enterprises; and in the artificial intelligence field, patent protection can be sought for almost at all the layers from the infrastructure layer, to the enabling technology layer, and then to the application layer. The subsequent sections will detail characteristics and difficulties of patent protection for respective layers in the field of artificial intelligence.
· Copyright (Ordinary Works, Software Copyright): It includes technical manual, product design drawing, and computer software code; algorithms and platform code suitable for the field of artificial intelligence. In addition, the copyright of ordinary works cannot be ignored. For example, Haier, after its "Call Firewall" were registered as written works, initiated copyright litigation against written works of other companies.
· Trademark: A large number of artificial intelligence systems, platforms, applications and products are entering the market. Trademarking is to obtain market monopoly through trademark registration before or after entering the market so that the trademark becomes a distinctive identifier of a product, thus helping to obtain market-identified monopoly, and such monopoly is a permanent one, which means that the monopoly exists as long as the enterprises require and that the monopoly will become a legal right against a third party.
· Domain Name: Given that artificial intelligence is currently so popular, domain names of ".ai" may become a new starting point for industry competition. Industry players will deploy domain names in line with their products, for example "drive.ai".
· Trade Secret: Details of key and core algorithms in the field of artificial intelligence can be protected as trade secrets.
· Data Protection and Compliance: Artificial intelligence needs to use a lot of training data in the process of machine learning. Training data can be gathered by oneself, be purchased from third-party data suppliers, or be captured from existing data through web crawlers. Training data must be acquired in accordance with the Civil Code, Cybersecurity Law, Data Security Law, Personal Information Protection Law, Anti-Unfair Competition Law and other applicable laws with legal methods so as to fully protect the legitimate rights and interests of the data and related data owners.
· Defensive Disclosure: Considering costs or the patentability of technical innovation, some of the technical contents that are not intended to be patented or that are not trade secrets could be disclosed in open source. "Time Stamp Authority (TSA)" provides public time stamp for defensive disclosure, and makes powerful prior art defense in litigation.
2.2.2 Exemplary Case of All-Round Protection Scheme for AI
Face++ is an open artificial intelligence platform developed by Megvii Technology, providing the world's leading computer vision services in the form of API or SDK. Products involve face detection, face analysis, face recognition, image recognition, OCR document recognition, and text recognition.
The face recognition technique of Face ++ is taken as an example here, and its all-round protection scheme includes patent, technical secret, copyright, and domain name.
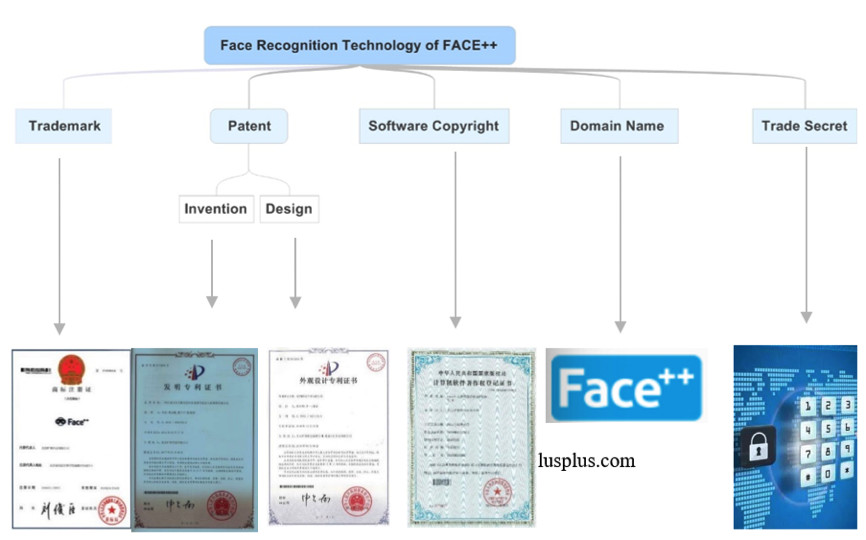
Fig. 2.2.2-1
2.3 Analysis on AI Patent Landscape
In terms of patent protection, the ownership of inventions and innovations can be determined through legal procedures, so as to effectively protect the results of inventions and innovations and monopolize the market to get in turn the greatest benefit. Therefore, patent protection is often the core in the above various intellectual property rights protection schemes.
In this part, by using the professional database IncoPat as the search database and through the fields in the title and abstract, the patent applications in the field of AI field in the world and in the major countries from January 1, 2010 to July 1, 2021 are searched and statistics.
Upon analysis of the search results, it can be found that AI, as one of the globally recognized scientific and technological development directions, has flourished globally.
2.3.1 Global AI Patent Application Trend and Layout
2.3.1.1 Global AI Patent Application Trend
From the number of artificial intelligence (AI) patent applications and the application-announcement trend in the world, it can be seen that the global AI patent applications are on the rise year by year[1], as shown in the following figures 2.3.1.1-1 and 2.2.1.1-2.
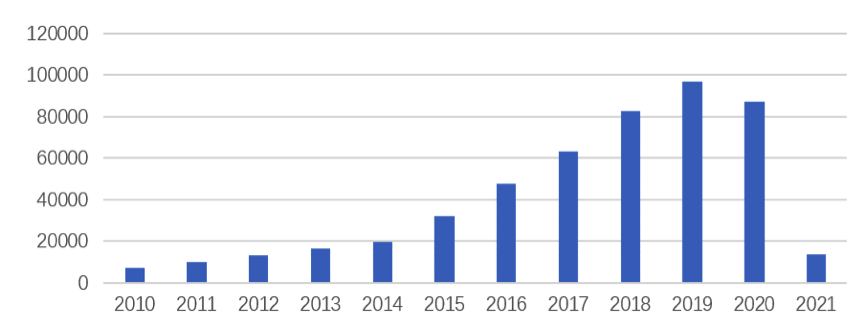
Fig. 2.3.1.1-1
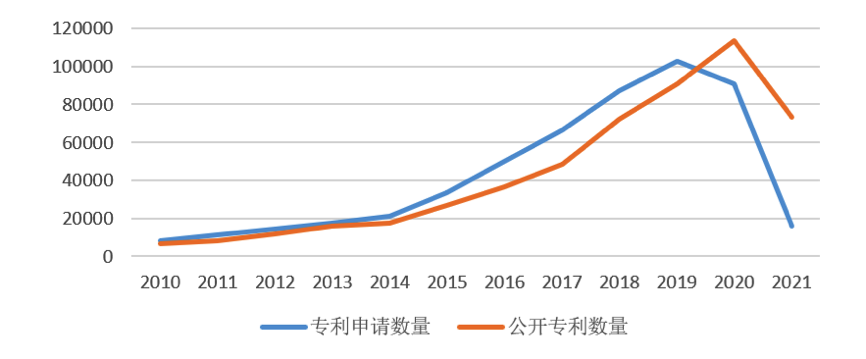
Fig. 2.3.1.1-2
[1]Due to the limitation on disclosure after 18 months, the data of 2020 and 2021 in this figure only includes a small part of the actual and announced applications in 2020 and 2021. The remaining data are not added up as they are not disclosed. The same as below.
2.3.1.2 Global AI Patent Application Layout
The analysis results of the number of global AI patent applications in various technical subject directions showed that the calculation system based on calculation model (G60N), electrical digital data processing (G06F), data recognition, data representation (G060K), and control and regulation system (G05B) are hot innovation fields, as shown in Figure 2.3.1.2 below.
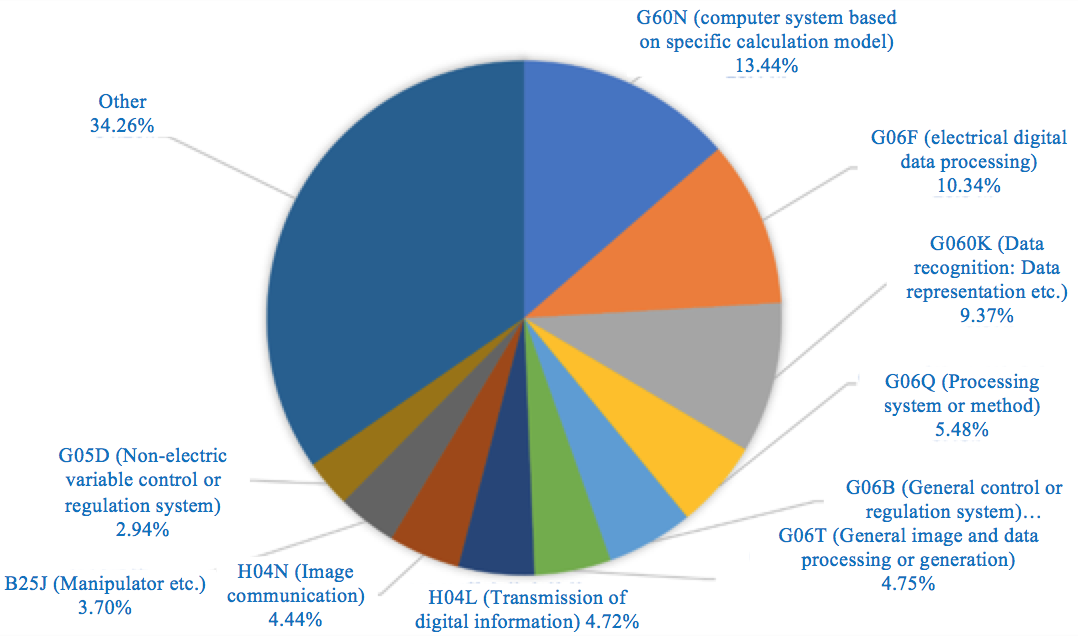
Fig. 2.3.1.2-1
2.3.2 AI Application Trend and Layout in Major Countries/Region
2.3.2.1 AI application Trend in Major Countries/Region
The following shows statistics on the number of patent applications of each major country/region in AI field. It can be seen from Figure 2.3.2.1 that currently, the global AI applications are mainly concentrated in China, the United States, Japan, South Korea and Europe. Among them, the number of patent applications in China was 384,116, ranking first in the world and clearly ahead of other countries/region.
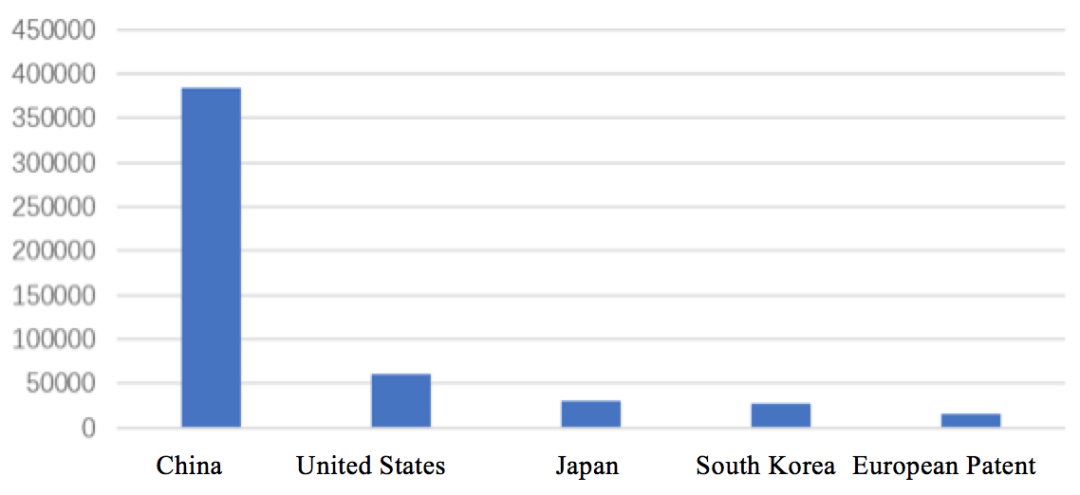
Fig. 2.3.2.1-1
2.3.2.2 Major Applicants
Statistics are made on the number of AI patent applications from 2010 to 2021. The following Figure 2.3.2.2-1 shows the ranking of the top ten applicants in the world. According to the following figures, the top ten organizations in the number of global AI patent applications are mainly concentrated in South Korea, the United States and China.
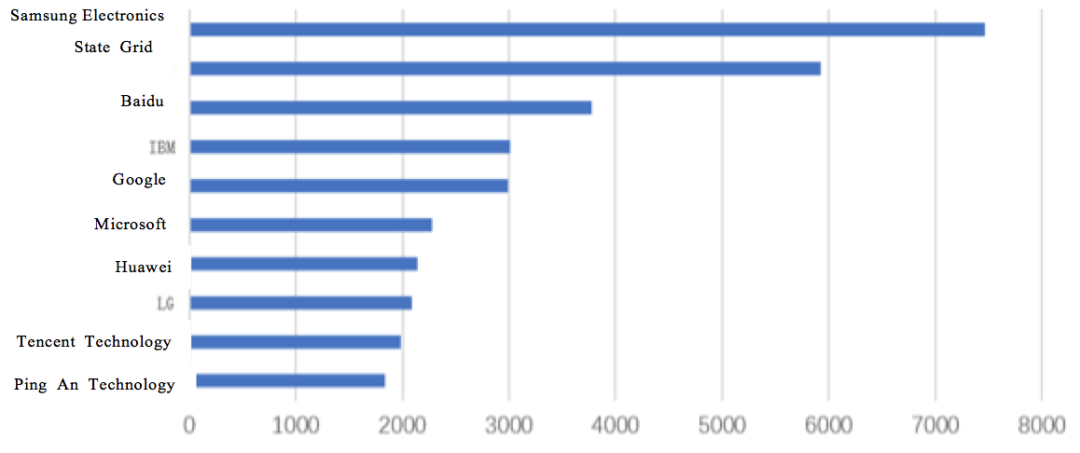
Fig. 2.3.2.2-1
The following Figure 2.3.2.2-2 shows the year-on-year application trend of the top ten major applicants. According to the following figures, the top ten organizations in the number of global AI patent applications are mainly concentrated in South Korea, the United States and China. Upon comparison of the number of global AI patent applications in each year, the application trend of the top ten applicants is generally the same as the global application trend. With the rapid increase in the number of applications filed by Chinese enterprises, China is becoming an important innovative force in the field of AI patent applications.
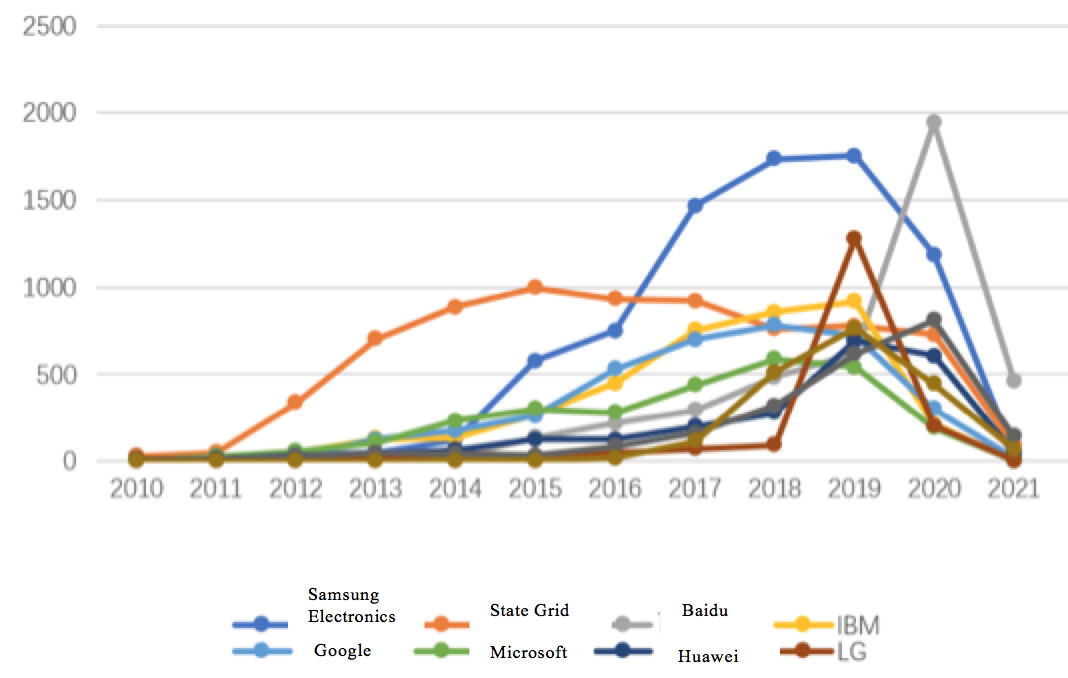
Fig. 2.3.2.2-2
2.3.2.3 AI Layout of Major Applicants
Figure 2.3.2.3 shows the distribution of patents in various technical fields of the world top ten applicants. It can be seen from the figure that Samsung Electronics has strong advantages in the field of transmission of digital information and computer systems based on specific calculation models. State Grid has obvious advantages in the field of control and regulation systems. Baidu is strong in data recognition, which is consistent with its search engine business. It can be seen from the technical themes applied for by enterprises that the enterprises mainly focus on the research related to their major business.
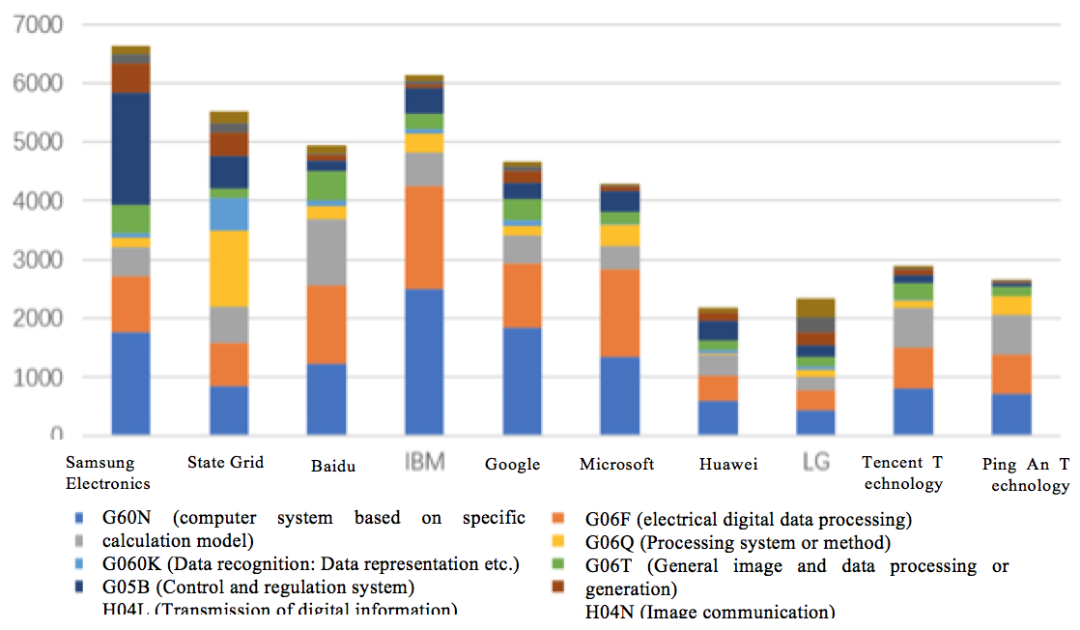
Fig. 2.3.2.3-1
2.3.3 AI Application and Layout in China
2.3.3.1 Analysis of Major Applicants in China
The top ten AI patent applicants in China are shown in Figure 2.3.3.1-1, including 5 enterprises and 5 colleges/universities. Currently, Internet enterprises and colleges/universities are the main force in the development of AI technology. State Grid ranks first in the number of applications, followed by Baidu, which shows that these two enterprises have strong advantages in AI field. In addition, colleges and universities also perform well in AI patent applications, with outstanding innovation capabilities.
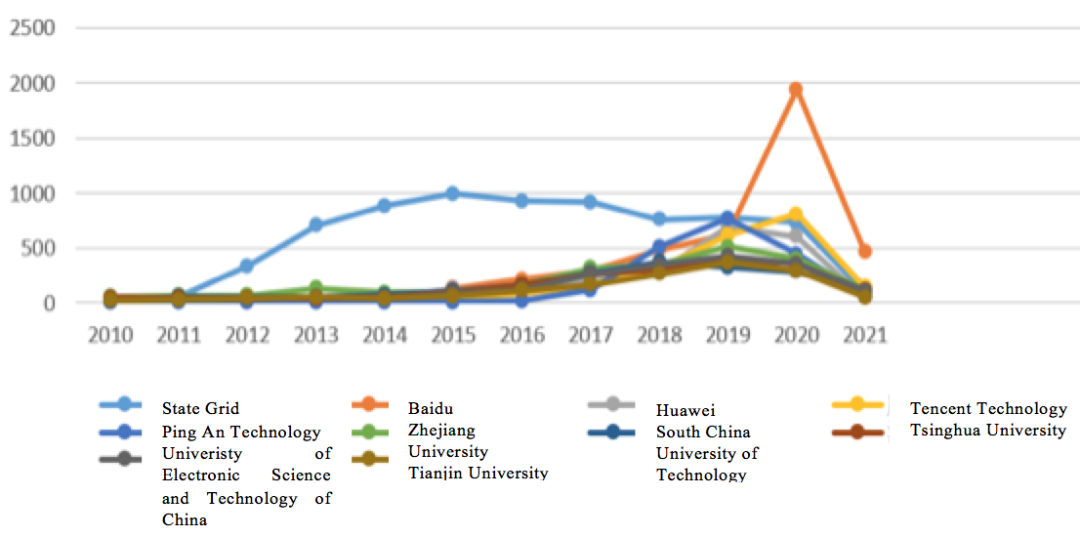
Fig. 2.3.3.1-1
Figure 2.3.3.1-2 shows the development trend of the number of patent applications filed by the top ten applicants in China. By comparing the patent application trends of each applicant, we can see that Internet enterprises show a rapid growth in the number of AI patent applications.
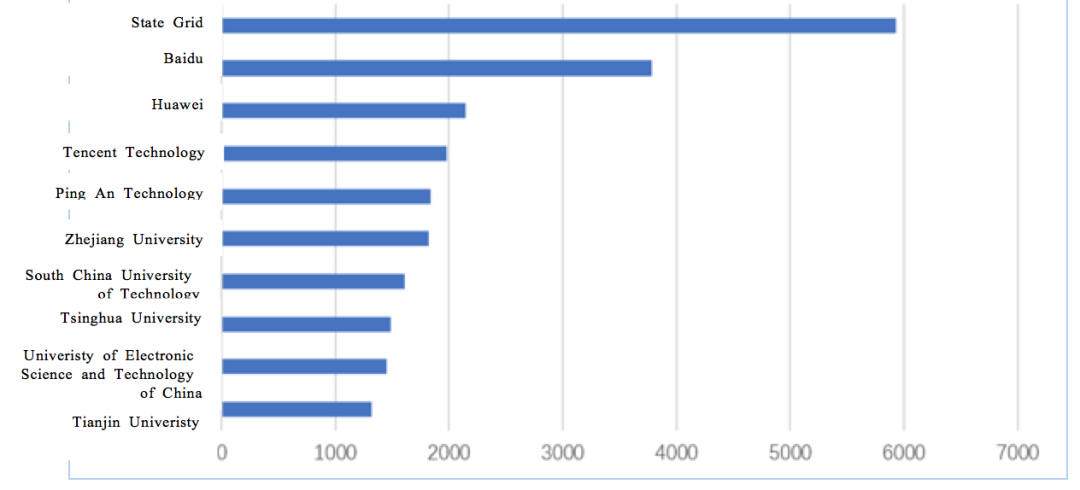
Fig. 2.3.3.1-2
2.2.3.2 AI Layout of Major Applicants in China
Chinese enterprises have great capabilities in fields of such as computer systems based on specific calculations, electrical digital data processing, data recognition, data representation, control and regulation system, and general image and data processing or generation. The AI research carried out by Chinese colleges and universities is relatively comprehensive, and their dominant technical fields are similar to those of Chinese enterprises. This makes the cooperation between Chinese enterprises and Chinese colleges/universities in promoting the innovation in AI field feasible, as shown in Figure 2.3.3.2 below.
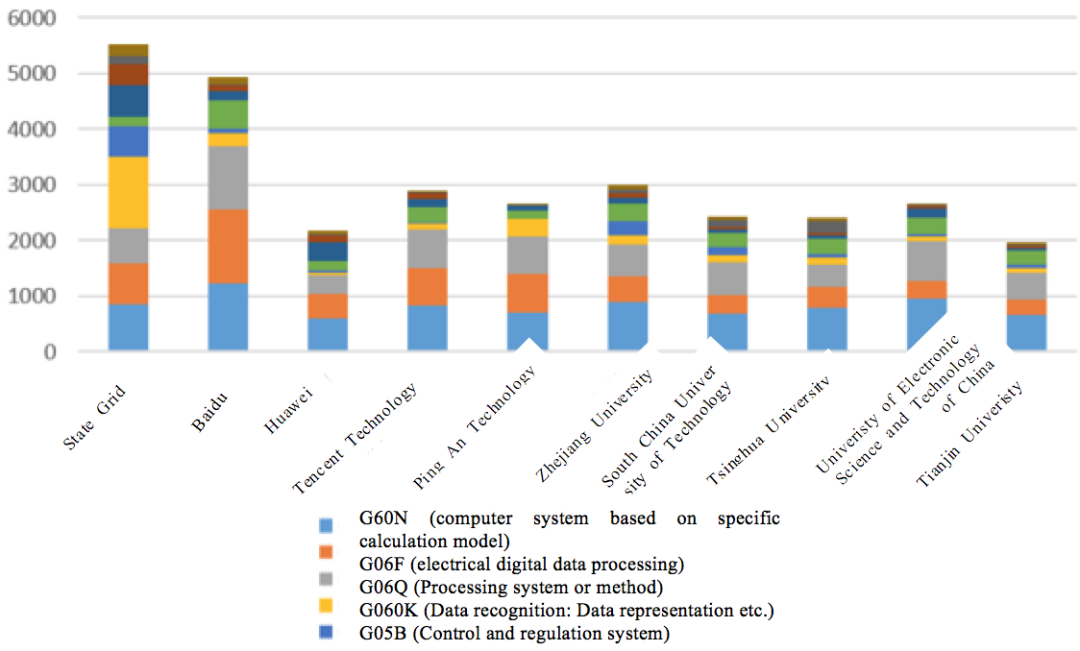
Figure 2.3.3.2



